Piston construction
Piston construction
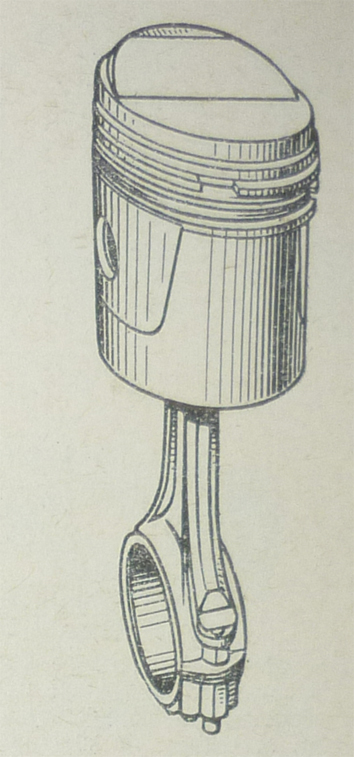
Figure 1 shows the main features of a piston construction. The crown forms the upper surface on which the gas pressure acts, and the force due to this pressure is equal to the cross-sectional area of the cylinder multiplied by the gas pressure. This force, which acts along the centre-line of the cylinder, is transmitted through the structure of the piston to the gudgeon pin bosses and thence through the gudgeon pin to the connecting rod.
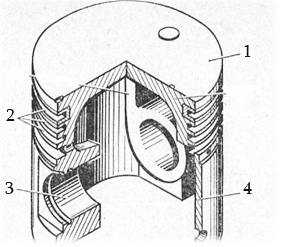
Piston construction
1 - crown, 2 - ring belt, 3 - gudgeon pin holes, 4 - skirt.
During the greater part of the stroke the connecting rod operates at an angle to the centre line of the cylinder. This causes a side force to be applied by the piston to the cylinder wall, and it is necessary to provide bearing surfaces on the piston to carry this side force: these bearing surfaces are formed on the skirt.
To allow the piston to move freely in the cylinder it must have some clearance. This in turn allows gas to leak the combustion chamber past the piston. Since the greatest leakage occurs when pressures are highest and the gas is hottest, much of the oil film lubricating the piston will be burnt away or carbonized. After combustion the gases contain water vapour, carbon dioxide and, probably, small amounts of sulphur dioxide which may contaminate the lubricating oil and lead to corrosion of the engine parts. To reduce the leakage as much as possible piston rings are fitted inti grooves formed on the piston just below the crown.
The crown of the piston is directly exposed to the full heat of the burning gases during combustion. These gases are still extremely hot during the power and exhaust strokes the piston absorbs a great deal of heat from these hot gases and will reach a very high temperature unless heat is removed from the piston quickly enough to keep its temperature within reasonable limits. The piston can pass this heat on to the cylinder walls through the piston rings and skirt, and it can do this better if the metal of which the piston is made is a good conductor of heat.
Most metals expand with a rise in temperature, and since the piston gets hotter than the cylinder (which can be cooled more effectively). Certain designs of combustion chamber require the piston crown to be made a particular shape, such as the domed crown.
Note that, whatever the shape of the crown, the effective force on the piston due to gas pressure is always given by the cross-sectional area of the cylinder bore.
Piston construction
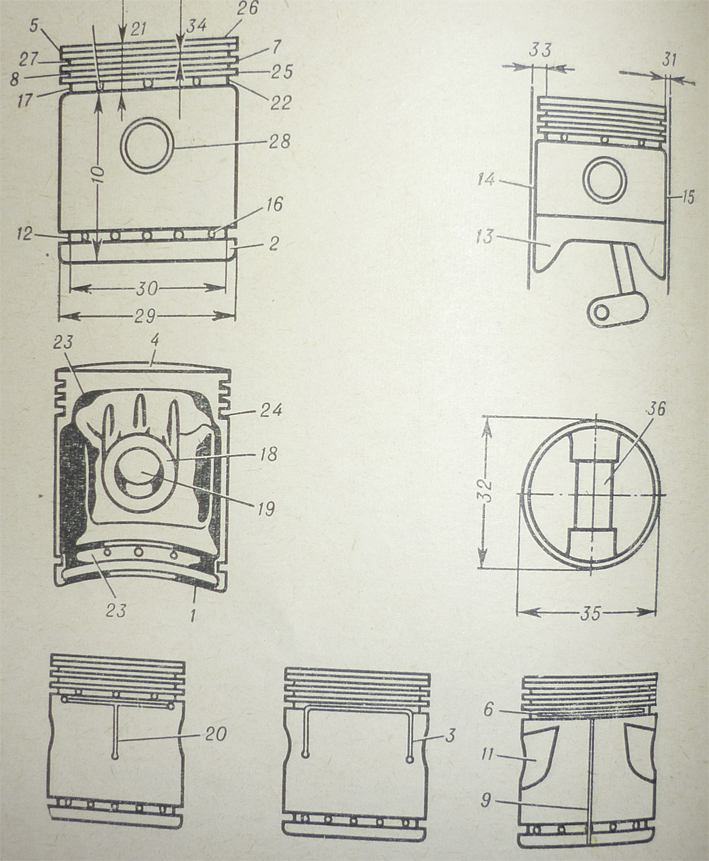
1 – bottom rib, 2 – chamfer, 3 – U-slot, 4 – head, 5 – heat dam, 6 – horizontal slot, 7 – second land, 8 – second-ring groove, 9 – vertical slot, 10 – skirt, 11 – skirt relief, 12 – skirt ring groove, 13 – slipper, 14 – major thrust face, 15 - minor thrust face, 16 – oil drain holes, 17 – oil-ring groove, 18 – pin-boss, piston pin boss, 19 – pin hole, 20 – T-slot, 21 – ring belt, 22 – ring groove bottom, 23 – ring groove pad, 24 – ring groove side, 25 – third land, 26 – top land, 27 – top-ring groove, 28 – pin bushing, 29 – land diameter, 30 – groove bottom diameter, groove root diameter, 31 – land clearance, 32 – minor diameter, 33 – groove depth, 34 – groove width, 35 – major diameter, 36 – piston pin, gudgeon pin.
Steel-belted piston
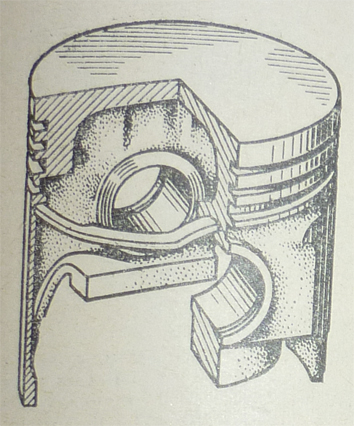
Step-head piston
Piston ring
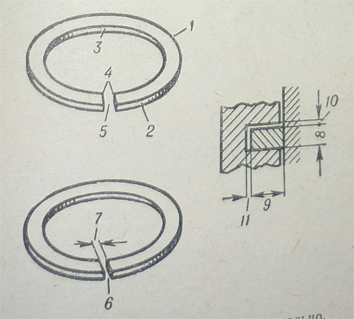
1 – side, top surface, 2 – face, 3 - back, 4 – ends, 5 – free gap, 6 – compressed gap, 7 – end clearance, 8 –width, 9 – radial thickness, 10 – side clearance, 11 – back clearance
Types of piston rings
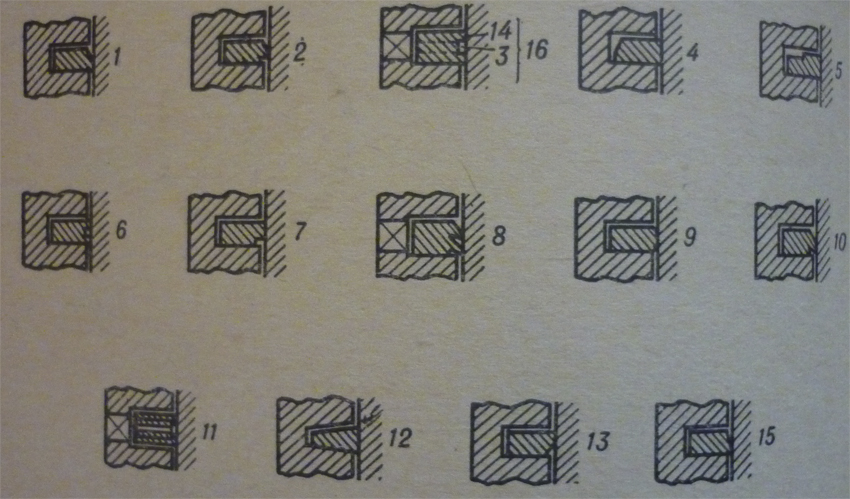
1 – bevel piston rings, 2 – bevel scraper piston rings, 3 – chanell of oil piston rings, 4 – inside bevel piston rings, 5 – counterbored piston rings, 6 – grooved piston rings, 7 – scraper, 8 – double-hook piston rings, 9 – double taper-faced piston rings, 10 – single-hook piston rings, 11 – multipiece piston rings, 12 – keystone piston rings, 13 – inverted bevel piston rings, 14 – flange of oil piston rings, 15 – taper-face piston rings, 16 – ventilated oil piston rings
Types of piston rings
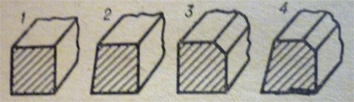
1 – straight-face piston rings, 2 – taper face piston rings, 3 – inside bevel piston rings, 4 – inside bevel taper face piston rings
Types of piston rings
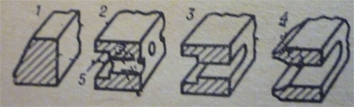
1 – bevel, 2 – drilled channel scraper, 3 – slotted channel oil, 4 – wedge channel grooved oil, 5 – channel of oil piston ring
Conformable oil piston ring, flexible oil piston ring, flexline oil piston ring
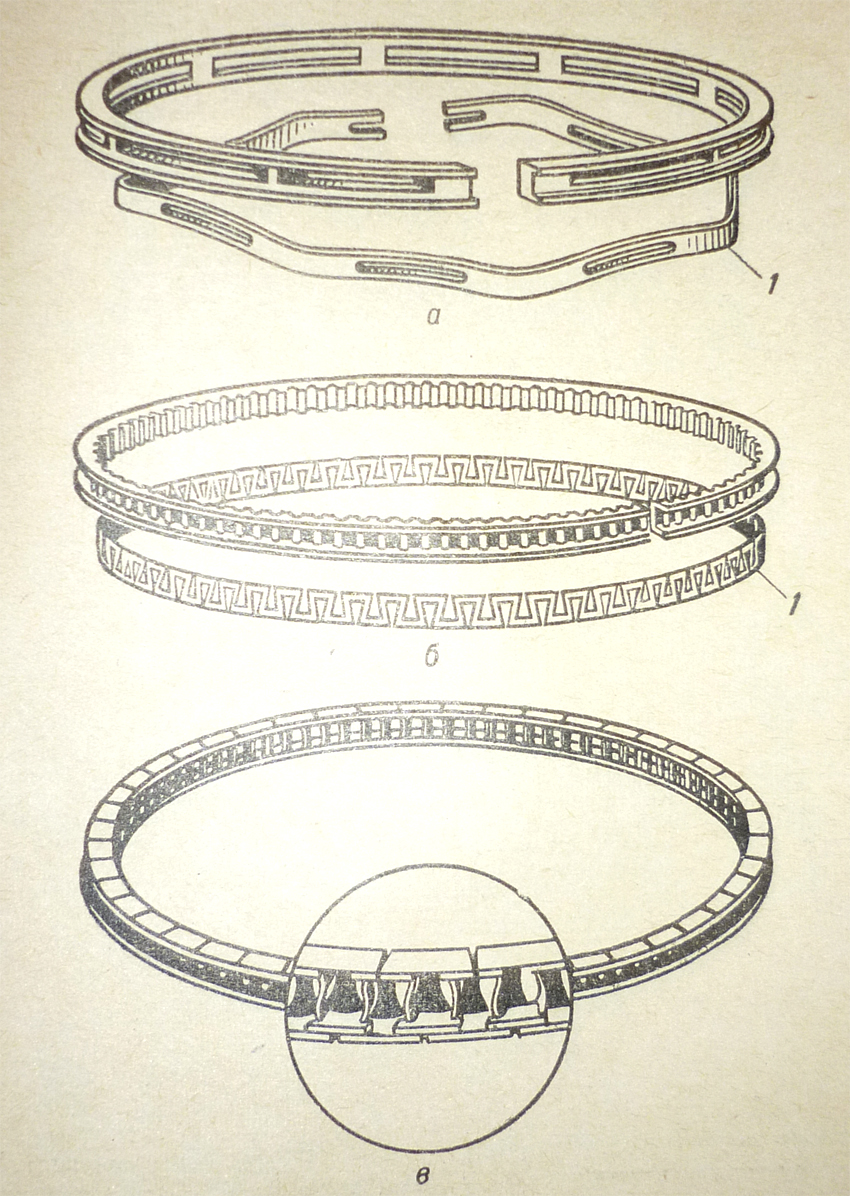
a– hump-type expander, б – cromflex oil piston ring, 1 – expander, в – circumferentially compressible piston ring
Piston pin
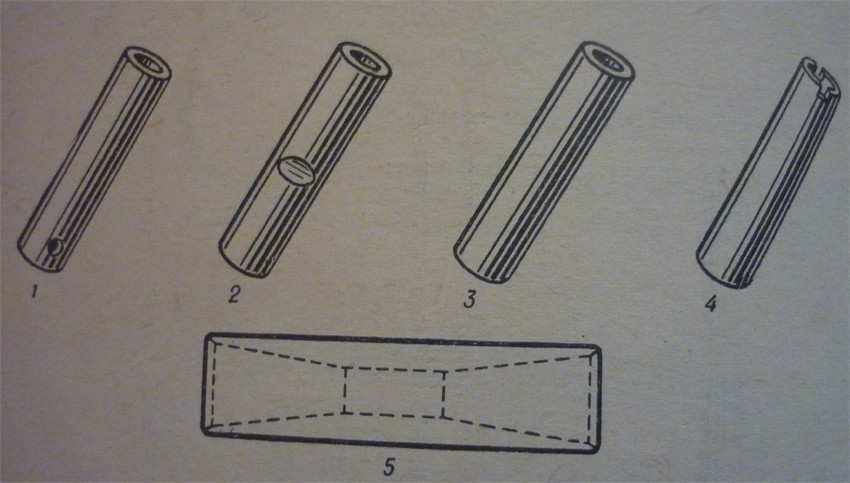
1 – set screw piston pin, 2 – semifloating piston pin, 3 – full-floating piston pin, 4 – end slot piston pin, 5 – piston pin with taper bore
Connecting rod big end
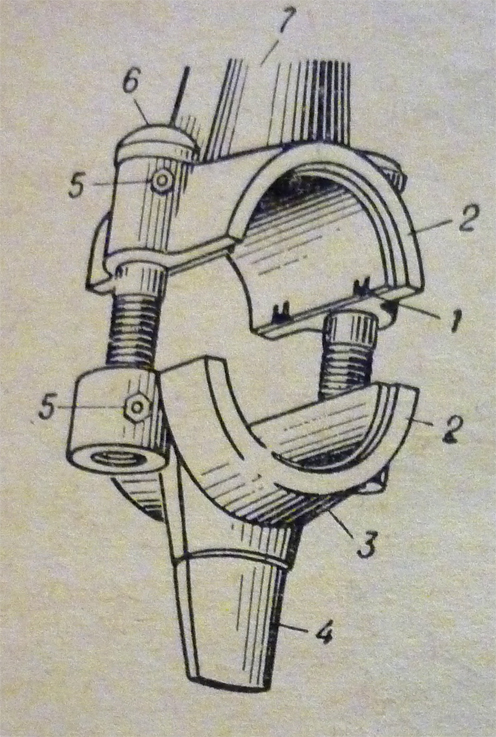
1 – connecting rod bushing lock, 2 – connecting rod big end bearing, 3 – connecting rod cap, 4 – connecting rod dipper, 5 – connecting rod and cap marks, 6 – big end bolt, 7 – connecting rod